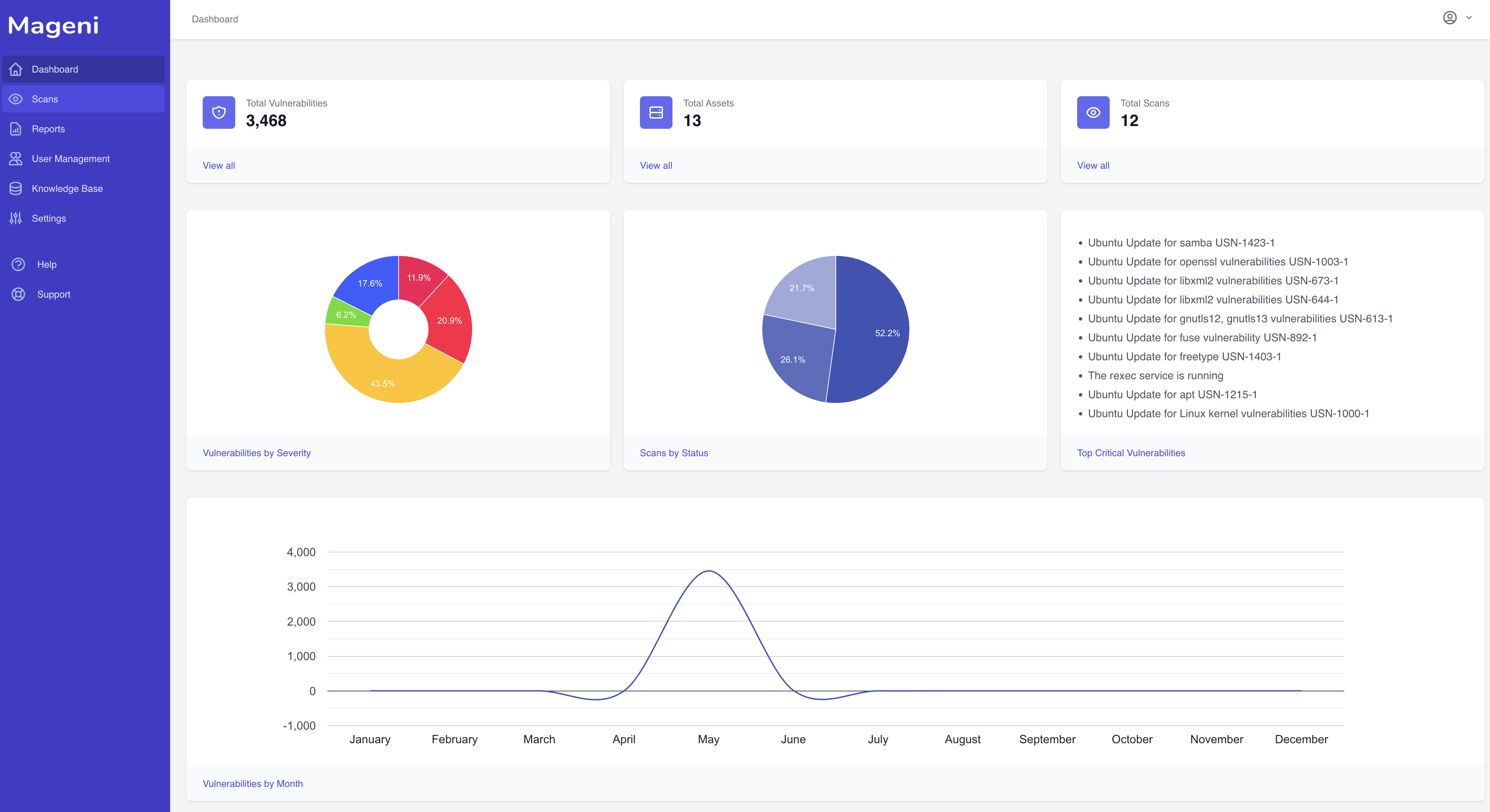
Free and open-source vulnerability scanner
Mageni eases for you the vulnerability scanning, assessment, and management process. It is free and open-source.
Install NowAvailable for macOS, Windows, and Linux
Huawei EulerOS: Security Advisory for dnsmasq (EulerOS-SA-2021-1733)
Information
Severity
Severity
Family
Family
CVSSv2 Base
CVSSv2 Base
CVSSv2 Vector
CVSSv2 Vector
Solution Type
Solution Type
Created
Created
Modified
Modified
Summary
The remote host is missing an update for the Huawei EulerOS 'dnsmasq' package(s) announced via the EulerOS-SA-2021-1733 advisory.
Insight
Insight
A flaw was found in dnsmasq. A heap-based buffer overflow was discovered in dnsmasq when DNSSEC is enabled and before it validates the received DNS entries. This flaw allows a remote attacker, who can create valid DNS replies, to cause an overflow in a heap-allocated memory. This flaw is caused by the lack of length checks in rfc1035.c:extract_name(), which could be abused to make the code execute memcpy() with a negative size in sort_rrset() and cause a crash in dnsmasq, resulting in a denial of service. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to system availability.(CVE-2020-25687) A flaw was found in dnsmasq. When receiving a query, dnsmasq does not check for an existing pending request for the same name and forwards a new request. By default, a maximum of 150 pending queries can be sent to upstream servers, so there can be at most 150 queries for the same name. This flaw allows an off-path attacker on the network to substantially reduce the number of attempts that it would have to perform to forge a reply and have it accepted by dnsmasq. This issue is mentioned in the 'Birthday Attacks' section of RFC5452. If chained with CVE-2020-25684, the attack complexity of a successful attack is reduced. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data integrity.(CVE-2020-25686) A flaw was found in dnsmasq. When getting a reply from a forwarded query, dnsmasq checks in forward.c:reply_query(), which is the forwarded query that matches the reply, by only using a weak hash of the query name. Due to the weak hash (CRC32 when dnsmasq is compiled without DNSSEC, SHA-1 when it is) this flaw allows an off-path attacker to find several different domains all having the same hash, substantially reducing the number of attempts they would have to perform to forge a reply and get it accepted by dnsmasq. This is in contrast with RFC5452, which specifies that the query name is one of the attributes of a query that must be used to match a reply. This flaw could be abused to perform a DNS Cache Poisoning attack. If chained with CVE-2020-25684 the attack complexity of a successful attack is reduced. The highest threat from this vulnerability is to data integrity.(CVE-2020-25685) A flaw was found in dnsmasq. When getting a reply from a forwarded query, dnsmasq checks in the forward.c:reply_query() if the reply destination address/port is used by the pending forwarded queries. However, it does not use the address/port to retrieve the exact forwarded query, substantially reducing the number of attempts an attacker on the network would have to perform to forge a reply and get it acce ... Description truncated. Please see the references for more information.
Affected Software
Affected Software
'dnsmasq' package(s) on Huawei EulerOS Virtualization release 2.9.1.
Detection Method
Detection Method
Checks if a vulnerable package version is present on the target host.
Solution
Solution
Please install the updated package(s).
